Tuesday, 23 August 2016
Thursday, 14 July 2016
Move VM files between datastore using PowerCLI
If you need to move VM folders from one datastore to another, you can do it easily using PowerCLI.
In this case, I had to move orphaned VMDK files and its folder from many different datastore to one temporary datastore. You can also use this script to Move ISO or any other files from one datastore to other datastore.
In below script specify your “destination-Datastore-name”
Create a csv file in c:\tmp\vmdk-folders.csv, with datastore and vmdkfolder headers. Under datastore column put the VM folder datastore name and in vmdkfolder column put VM folder path.
|
Connect-VIServer vcenter-server $dstDatastore = Get-Datastore destination-Datastore-Name New-PSDrive -PSProvider VimDatastore -Root "\" -location $dstDatastore -Name dstDS $vmdks = Import-Csv c:\temp\vmdk-folders.csv foreach ( $vmdk in $vmdks ) { Write-Host Moving $vmdk.vmdkfolder from $vmdk.datastore.... $srcDatastore = Get-Datastore $vmdk.datastore $vmdkfolder = $vmdk.vmdkFolder New-PSDrive -PSProvider VimDatastore -Root "\" -location $srcDatastore -Name srcDS Move-Item srcDs:\$vmdkfolder -Destination dstDS:\ Remove-PSDrive -Name srcDS }
|
If you want to just copy VM or VM files from one datastore to another datastore or download files to local computer then replace Move-Item command with Copy-Item or Copy-DatastoreItem command.
Also You can change source and destination as needed.
Thanks,
vPRH
Wednesday, 1 June 2016
How to Install VMware Update Manager
This post is part of VMware vSphere Install, Configure, Manage training series.
VMware vSphere: Install, Configure, Manage
See previous Post for introduction of VMware Update manager - vSphere Update Manager and Host Maintenance
In this post, we will see How to install VMware Update manager and integrate it with vCenter Appliance or vCenter server Installed on Windows System. As mentioned in previous post, vCenter Appliance don’t come with embedded Update manager so we need to install Update manager on separate Windows 64-bit System and Integrate it with vCenter Appliance.
Prerequisite – Install Windows 64-bit on Physical or Virtual server, Do network settings, Add system in Domain and do any other settings as you do for any other Windows server system.
Make sure vCenter, ESXi and Update manager system communicate with each other on Port 80, 443, 802, 902, 9084, 9087.
Step by Step Installation of VMware Update Manager
1. Login to Windows Server where you wish to install Update manager.
2. Setup DSN
If you decide to use embedded SQL Server 2012 Express then you can skip this step.
If you choose to use external SQL Database, you need to first install SQL Native Client driver and setup 32bit ODBC DSN.
Download and install ODBC Native client Driver on Update manager server system.
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=30440
Download sqlncli_x86.msi and install it.
3. If you choose to go with external SQL server DB, Please login to SQL Server and create SQL DB to use for update manager. Skip this step if you decide to use SQL Express bundled with Update manager.
4. Create ODBC DSN for Update manager
- Open Run menu and Type \Windows\SysWOW64\odbcad32.exe and hit enter.
- It will start ODBC data source Administrator 32 bit configuration.
- Click on System DSN menu
- Click Add
- Scroll down and Select SQL Server Native Client
- Click on Finish. This will launch DSN creation Window.
- In Create a New Data Source to SQL Server Window, Enter below details
- Name – Name of DSN
- Description – small description for this DSN
- Server - Enter name of SQL server and instance name where update manager database you want to create.
- Click Next Once you enter above details.
- On next screen, Select how you want to authenticate with SQL server.
- SQL Authentication with Integrated Windows Authentication is preferred.
- You can also use SQL server Authentication, Enter sql account username/password below if you choose to.
- In Below Image am using Integrated Windows Authentication..
- Click Next
- Select checkbox to Change the default database to
- From the drop down menu, select the database name which you have created in Step 3.
- On the next screen, review the DSN settings and click on Finish.
- Test Data source settings and Click on OK –> OK to close all Windows.
5. Mount or extract VMware vCenter ISO file on Update manager system. You need to use the ISO of vCenter installer for Windows.
6. Double Click on Autorun.exe for to launch vCenter Installer.
7. From vSphere Update Manager Select Server to Install. If you choose to use Microsoft SQL Server 2012 Express as DB then select the Checkbox next to Embedded data base option.
In this post, we are using external SQL server
Click Install
8. Select Language and Click on OK
9. if .Net Framework 3.5 is not installed on system, installer will prompt you.
Click on OK to install .Net Framework 3.5
10. Click Next on welcome screen.
11. Accept the terms in the license agreement if you wish to and then Click Next.
12. You can uncheck Download updates from default sources after installation and click Next.
13. Enter vCenter connection information
- IP Address/name – Enter vCenter IP or Hostname
- HTTP Port – 80 keep it default
- Username – Username who has Administrator permissions on vCenter server.
- Password – vCenter user password.
- Click Next Once done.
14. Select the DSN name which you have created in Step 3, if you don’t see the DSN name here, make sure you have created DSN in 32-bit ODBC. Cancel installation and perform step 3 first and then again start installation.
Click Next to proceed.
15. Click Next on database information page.
Click on OK to Ignore the warning message if you receive for SQL recovery mode.
16. On Update Manager Port settings select How this update manager should be identified in Network i.e. by name or IP, Keep the default ports and Click Next.
17. Note the destination folder to install update manager and patch download folder, change folder location if you wish and Click Next to proceed
18. If you have less than 120 GB free space on patch download folder location, you will receive warning message, Click OK to ignore it.
19. Click on Install to start the installation of VMware vSphere Update Manager.
watch the installation process.
20. Once installation gets completed click on Finish.
21. Run Update Manager service with Windows Accounts.
Launch services.msc in Windows system on Update manager server.
Select VMware vSphere Update Manager service and go to Properties.
Click on Log On –> This Account
enter domain user name and password by which you want to run this server.
Make sure this domain account has Administrator privileges on this VUM server system.
Click o OK and restart Update manager service.
With this we have successfully installed VMware Update Manager.
See Next post to configure Update manager settings and download Patches, schedule patch Alerts.
Next - How to Configure Update manager settings
Home - VMware vSphere: Install, Configure, Manage
Thanks
vPRH
vSphere Update Manager and Host Maintenance
This post is part of VMware vSphere Install, Configure, Manage training series.
VMware vSphere: Install, Configure, Manage
VMware Update manager provides functionality to Install ESXi updates, Install ESXi Patches, Upgrade ESXi Host, Install third party software packages on ESXi Host.. Using VMware Update manager you can also automate Upgrade of VMware tools and Virtual Machine hardware version for VMs.
Once you install VMware vCenter and is ready to use then Install VMware Update manager and integrate it with vCenter server. Update manager cannot be used without vCenter server.
Update manager can be installed on same Windows system as vCenter Server. As of with vCenter Appliance 6.0 update 2, Update manager is not bundled with Appliance vCenter system. So we need to install VMware update manager on separate Windows system and integrate it with vCenter Appliance.
In this post we will be installing VMware Update manager on Windows System and integrating it with vCenter Appliance 6.0 Update 2.
Hardware Requirements
- 1 vCPU
- 2 GB RAM
- Disk – 80 GB
Operating System – Update manager 5.5 and above requires 64-bit Windows server 2008 or 2012 Operating systems.
Database – Update manager supports Microsoft SQL or Oracle database. For small environment you can also use Embedded SQL server 2012 express.
DSN connectivity – On 64-bit operating system you need to create DSN in 32-bit ODBC driver (\Windows\SysWOW64\odbcad32.exe).
See Next Post
- How to Install VMware Update Manager
- How to Configure Update manager settings
- How to Install ESXi Patches using Update manager
- How to Upgrade ESXi Host using Update manager
- What is Update Manager utility
Thanks,
vPRH
Home - VMware vSphere: Install, Configure, Manage
Next - How to Install VMware Update Manager
VMware FT error Device 'Hard Disk 1' uses a controller that is not supported
Error – When you try to enable Fault Tolerance on VMware VM you receive below error.
Device 'Hard Disk 1' uses a controller that is not supported
{reason.@enum.fault.DeviceNotSupported.Reason}
Reason
This error occurs if you are using IDE Disk controller for VM.
IDE disk controllers are not supported by VMware FT and you have to use only SCSI controllers for VMs.
Solution
Change VM disk controllers from IDE to SCSI. If you change disk controller from IDE to SCSI, it will make your Guest OS unusable.
So you need to create new VM with scsi disks, Install Guest OS and then enable FT.
If you want to enable FT on Existing VM with IDE disk then you need to do V2V conversion using VMware Convertor.
Follow below KB to convert non-OS IDE Disk to SCSI.
Thanks…!
Tuesday, 31 May 2016
Error while performing Cert Replacement operation for vCenter 6
While replacing SSL certificates of vCenter 6, Certificate replacement may fail and VMCA rollback the certificates to old SSL certificates.
See the complete process of replacing SSL certificates of vSphere 6 using VMCA.
Replacing SSL Certificates VMware vCenter 6.0 Update 2.
In this Post am documenting common issues which you may encounter while performing SSL certificates replacement.
1. See this KB for list of errors which you may encounter.
To avoid issues with vCenter services, make sure you provide unique organization unit name while creating Certificate configuration file.
You can use below Organization Unit name for SSL certificates.
MACHINE_SSL_CERT.cfg : Root
machine.cfg : Machine
vsphere-webclient.cfg : WebClient
vpxd.cfg : VPXD
vpxd-extension.cfg : VPXD-EXT
certool.cfg : IT-VMCA
2. Error while performing Cert Replacement operation, please see /var/log/vmware/vmcad/certificate-manager.log for more information.
You can see below Error message in /var/log/vmware/vmcad/certificate-manager.log
2016-05-28T22:12:54.141Z INFO certificate-manager Running command :- ['/usr/lib/vmware-vmca/bin/certool', '--server=localhost', '--gencert', '--privkey=/storage/certmanager/vpxd.priv', '--cert=/storage/certmanager/vpxd.crt', '--config=/var/tmp/vmware/vpxd.cfg']
2016-05-28T22:12:54.153Z INFO certificate-manager Command output :-
Using config file : /var/tmp/vmware/vpxd.cfg
2016-05-28T22:12:54.153Z ERROR certificate-manager Using config file : /var/tmp/vmware/vpxd.cfg
2016-05-28T22:12:54.153Z ERROR certificate-manager Error while performing Cert Replacement operation, please see /var/log/vmware/vmcad/certificate-manager.log for more information.
2016-05-28T22:12:54.153Z ERROR certificate-manager {
"resolution": null,
"detail": [
{
"args": [
"Using config file : /var/tmp/vmware/vpxd.cfg\n"
],
"id": "install.ciscommon.command.errinvoke",
"localized": "An error occurred while invoking external command : 'Using config file : /var/tmp/vmware/vpxd.cfg\n'",
"translatable": "An error occurred while invoking external command : '%(0)s'"
},
"Error in generating cert for store vpxd"
],
"componentKey": null,
"problemId": null
}
You will receive this error if your SSL certificate configuration file is incorrect and then VMCA will rollback certificates.
Solution
Login to vCSA using SSH with root user.
Go to /var/tmp/vmware directory, Create temporary directory and move all .cfg configuration files to temp directory, later on you can remove these files.
#cd /var/tmp/vmware
#mkdir temp
#mv *.cfg temp
Now run the certificate-manager command once again and start Certificate replacement process.
Follow Replacing SSL Certificates VMware vCenter 6.0 Update 2 to replace SSL certificates.
Thanks…!
Monday, 30 May 2016
Replacing SSL Certificates VMware vCenter 6.0 Update 2
SSL certificates are the one of the most important part in VMware vCenter server and VMware ESXi. All traffic between ESXi Host, vCenter and between all vCenter services are encrypted using SSL certificates. Over the time VMware has improved the process to replace SSL certificates for different vCenter components.
If you need to update SSL certificates of vCenter 6.0 then you can follow below KB to replace certificates.
However the process to replace SSL certificate of vCenter 6.0 Update 1b is changed and is not well documented, so let’s See How to Replace SSL Certificates of VMware vCenter 6.0 Update 2.
In VMware vCenter 6 VMware has introduced VMware Certificate Authority (VMCA), We are going to make this VMCA as an intermediate CA of our Internal Corporate Microsoft CA server. Then VMCA will take care of replacing SSL certificates of different vCenter services and also it will issue certificates to ESXi Hosts which you add in vCenter.
Important – In vSphere SSL configuration OrgUnit need to be unique for each service or certificate replacement will fail.
In this process, we will be using below Organization Unit for vCenter services.
MACHINE_SSL_CERT.cfg : Root
machine.cfg : Machine
vsphere-webclient.cfg : WebClient
vpxd.cfg : VPXD
vpxd-extension.cfg : VPXD-EXT
certool.cfg : IT-VMCA
See this Post for common issues during certificate replacement.
Error while performing Cert Replacement operation for vCenter 6
How to make VMCA as Intermediate CA?
1. Login to VMware vCenter Appliance using SSH with root username and password. You can use Putty utility to login to Linux system using SSH.
You need to have ssh enabled on vCenter Appliance.
Follow this document to enable SSH on vCenter server, if it is not enabled already.
http://blog.ukotic.net/2015/06/14/enable-ssh-on-vcenter-server-appliance-6-vcsa/
2. Once you logged in to vCSA using SSH, enable shell access with below commands
>shell.set --enabled True
>shell
3. Edit cartool.cfg file
#cd /usr/lib/vmware-vmca/share/config
backup cartool.cfg file before editing, so that you can revert back to original if needed.
#cp certool.cfg certool.cfg.bak
#vi certool.cfg
Press i to enter in edit mode.
Move cursor to specific line and edit details as below, Press Esc key and then :wq to save and close the file.
#
# Template file for a CSR request
#
# Country is needed and has to be 2 characters
Country = US
Name = vlab-vc01.vprhlabs.com
Organization = your-ognization-name
OrgUnit = IT
State = Missouri
Locality = Raytown
IPAddress = 192.168.10.10
Email = vprh@vprhlabs.com
Hostname = vlab-vc02.vprhlabs.com
4. Execute certificate-manager command to start SSL Certificate replacement process.
#/usr/lib/vmware-vmca/bin/certificate-manager
5. Select option 2 to Replace VMCA Root certificate with Custom Signing Certificate and replace all Certificates and Press Enter.
Follow the prompt and provide your inputs, I have highlighted my inputs. Also to accept the default values [values in name bracket] press Enter
6. Do you wish to generate all certificates using configuration file : Option[Y/N] ? : Y
7. Please provide valid SSO and VC priviledged user credential to perform certificate operations.
Enter username [Administrator@vsphere.local]:
Enter password:**** you cannot see password * characters on Linux, enter correct password.
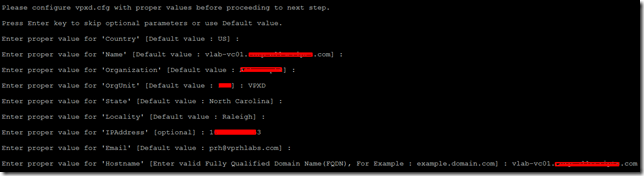
8. Please configure MACHINE_SSL_CERT.cfg with proper values before proceeding to next step.
Press Enter key to skip optional parameters or use Default value.
- Enter proper value for 'Country' [Default value : US] :
- Enter proper value for 'Name' [Default value : vlab-vc01.vprhlabs.com] :
- Enter proper value for 'Organization' [Default value : vPRHLABS] :
- Enter proper value for 'OrgUnit' [Default value : ITS] : Root
- Enter proper value for 'State' [Default value : North Carolina] :
- Enter proper value for 'Locality' [Default value : Raleigh] :
- Enter proper value for 'IPAddress' [optional] : 192.168.105.10
- Enter proper value for 'Email' [Default value : prh@vprhlabs.com] :
- Enter proper value for 'Hostname' [Enter valid Fully Qualified Domain Name(FQDN), For Example : example.domain.com] : vlab-vc01.vprhlabs.com
Continue the the wizard to create machine.cfg file.
9. Please configure machine.cfg with proper values before proceeding to next step.
Press Enter key to skip optional parameters or use Default value.
- Enter proper value for 'Country' [Default value : US] :
- Enter proper value for 'Name' [Default value : vlab-vc01.vprhlabs.com] :
- Enter proper value for 'Organization' [Default value : vPRHLABS] :
- Enter proper value for 'OrgUnit' [Default value : ITS] : Machine
- Enter proper value for 'State' [Default value : North Carolina] :
- Enter proper value for 'Locality' [Default value : Raleigh] :
- Enter proper value for 'IPAddress' [optional] : 192.168.105.10
- Enter proper value for 'Email' [Default value : prh@vprhlabs.com] :
- Enter proper value for 'Hostname' [Enter valid Fully Qualified Domain Name(FQDN), For Example : example.domain.com] : vlab-vc01.vprhlabs.com
Continue the the wizard, to create vsphere-webclient.cfg file.
10. Please configure vsphere-webclient.cfg with proper values before proceeding to next step.
Press Enter key to skip optional parameters or use Default value.
- Enter proper value for 'Country' [Default value : US] :
- Enter proper value for 'Name' [Default value : vlab-vc01.vprhlabs.com] :
- Enter proper value for 'Organization' [Default value : vPRHLABS] :
- Enter proper value for 'OrgUnit' [Default value : ITS] : WebClient
- Enter proper value for 'State' [Default value : North Carolina] :
- Enter proper value for 'Locality' [Default value : Raleigh] :
- Enter proper value for 'IPAddress' [optional] : 192.168.105.10
- Enter proper value for 'Email' [Default value : prh@vprhlabs.com] :
- Enter proper value for 'Hostname' [Enter valid Fully Qualified Domain Name(FQDN), For Example : example.domain.com] : vlab-vc01.corp.allscripts.com
Please configure vpxd.cfg with proper values before proceeding to next step.
11. Press Enter key to skip optional parameters or use Default value.
- Enter proper value for 'Country' [Default value : US] :
- Enter proper value for 'Name' [Default value : vlab-vc01.vprhlabs.com] :
- Enter proper value for 'Organization' [Default value : vPRHLABS] :
- Enter proper value for 'OrgUnit' [Default value : ITS] : VPXD
- Enter proper value for 'State' [Default value : North Carolina] :
- Enter proper value for 'Locality' [Default value : Raleigh] :
- Enter proper value for 'IPAddress' [optional] : 192.168.105.10
- Enter proper value for 'Email' [Default value : prh@vprhlabs.com] :
- Enter proper value for 'Hostname' [Enter valid Fully Qualified Domain Name(FQDN), For Example : example.domain.com] : vlab-vc01.vprhlabs.com
Continue the wizard to create vpxd-extension.cfg
12. Please configure vpxd-extension.cfg with proper values before proceeding to next step.
Press Enter key to skip optional parameters or use Default value.
- Enter proper value for 'Country' [Default value : US] :
- Enter proper value for 'Name' [Default value : vlab-vc01.vprhlabs.com] :
- Enter proper value for 'Organization' [Default value : vPRHLABS] :
- Enter proper value for 'OrgUnit' [Default value : ITS] :VPXD-EXT
- Enter proper value for 'State' [Default value : North Carolina] :
- Enter proper value for 'Locality' [Default value : Raleigh] :
- Enter proper value for 'IPAddress' [optional] : 192.168.105.10
- Enter proper value for 'Email' [Default value : prh@vprhlabs.com] :
- Enter proper value for 'Hostname' [Enter valid Fully Qualified Domain Name(FQDN), For Example : example.domain.com] : vlab-vc01.vprhlabs.com
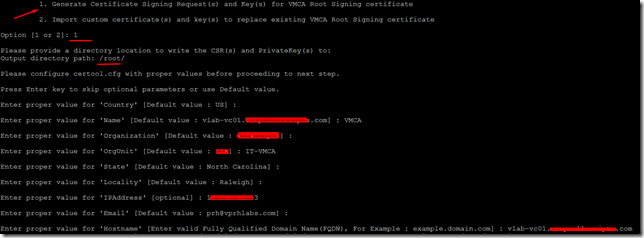
13. Continue the wizard and select option 1 to generate Certificate Signing request and key for VMCA root certificate.
- 1. Generate Certificate Signing Request(s) and Key(s) for VMCA Root Signing certificate
- 2. Import custom certificate(s) and key(s) to replace existing VMCA Root Signing certificate
Option [1 or 2]: 1
14. Please provide a directory location to write the CSR(s) and PrivateKey(s) to:
Output directory path: /root/
15. Please configure certool.cfg with proper values before proceeding to next step.
- Press Enter key to skip optional parameters or use Default value.
- Enter proper value for 'Country' [Default value : US] :
- Enter proper value for 'Name' [Default value : vlab-vc01.vprhlabs.com] : VMCA
- Enter proper value for 'Organization' [Default value : vPRHLABS] :
- Enter proper value for 'OrgUnit' [Default value : ITS] : IT-VMCA
- Enter proper value for 'State' [Default value : North Carolina] :
- Enter proper value for 'Locality' [Default value : Raleigh] :
- Enter proper value for 'IPAddress' [optional] : 192.168.105.10
- Enter proper value for 'Email' [Default value : prh@vprhlabs.com] :
- Enter proper value for 'Hostname' [Enter valid Fully Qualified Domain Name(FQDN), For Example : example.domain.com] : vlab-vc01.vprhlabs.com
16. This will generate Certificate Signing request (CSR) and key for VMCA certificate and store at the location specified e.g. /root/ as specified above.
2016-05-30T16:51:51.299Z Running command: ['/usr/lib/vmware-vmca/bin/certool', '--genkey', '--privkey', '/root/vmca_issued_key.key', '--pubkey', '/tmp/pubkey.pub']
2016-05-30T16:51:51.937Z Done running command
2016-05-30T16:51:51.937Z Running command: ['/usr/lib/vmware-vmca/bin/certool', '--gencsr', '--privkey', '/root/vmca_issued_key.key', '--pubkey', '/tmp/pubkey.pub', '--config', '/var/tmp/vmware/certool.cfg', '--csrfile', '/root/vmca_issued_csr.csr']
2016-05-30T16:51:52.343Z Done running command
CSR generated at: /root/vmca_issued_csr.csr
17. Keep the putty session running, don’t close it.
18. Login to vCenter Appliance using WinSCP and download the CSR file on your local system.
18.1. To access vCSA using WinSCP, you need to first set root shell to bash.
18.2. Open one more Putty session and login to vCenter Appliance with root user and password.
>shell.set --enabled True
>shell
#chsh -s /bin/bash root
18.3 Now Download and install WinSCP on your system.
18.4 Launch WinSCP, Enter IP or Hostname of vCenter system, Enter username and password and connect to vCenter.
18.5 Download /root/vmca_issued_csr.csr file from vCSA server to your local system.
19. Submit CSR file to your Certificate Authority to receive SSL certificate.
If you are using Microsoft CA of your organization then first you need to have certificate Template configured which can be used to issue certificates for Intermediate CA or Subordinate CA.
In My testing setup, am using Internal Microsoft Certificate Authority to issue certificate to VMCA. Make sure you have access to use that certificate template.
Get the CA certificate from Certificate Authority.
19.1 Open Command prompt and Change to the directory where you have downloaded CSR file.
>cd F:\tmp\vlab-vc01
>certreq -submit -config "CAServer\CAServer" -attrib "CertificateTemplate:VMCAIntermediateCA" vmca_issued_csr.csr vlab-vc01-CA.crt
- VMCAIntermediateCA is the name of my SSL certificate Template for VMware in Microsoft CA.
- CAServer – is name of CA server, replace this value with your CA server name.
Alternatively, you can visit the CA URL and request SSL certificate.
19.2 Also you need to download complete Chain of ROOT CA certificates chain.
20. Create a Certificate chain using VMCA certificate, Intermediate CA and root CA certificate.
Open Command prompt and change to directory where you have saved all certificates.
>copy vlab-vc01-VMCA.cer+root64-2.cer+root64-1.cer root_signing_chain.cer
- root64-2.cer – is first intermediate Certificate of CA
- root64-1.cer – is root CA certificate.
You can also open certificate files using Notepad++ and copy/paste VMCA certificate, Intermediate and root CA’s certificate to create certificate chain.
Note, while copying certificate, there should not be any empty lines and you should follow below certificate sequence otherwise certificate replacement will not work.
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
Copy VMCA certificate here
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
Copy Intermediate CA certificate here
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
Copy Root CA certificate here
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
save this certificate chain file in root_signing_chain.cer file, make sure there are no empty lines or you don’t add any extra characters.
21. Upload Certificate chain to vCSA server /root/ location using WinSCP.
22. Now, go back to first Putty session where we start the certificate-manager to replace certificate.
23. Press 1 to Import VMCA certificate
- 1. Continue to importing Custom certificate(s) and key(s) for VMCA Root Signing certificate
- 2. Exit certificate-manager
Option [1 or 2]: 1
24. Please provide valid custom certificate for Root.
File : /root/root_signing_chain.cer
Please provide valid custom key for Root.
File : /root/vmca_issued_key.key
25. You are going to replace Root Certificate with custom certificate and regenerate all other certificates
Continue operation : Option[Y/N] ? : Y
This will import the VMCA certificate chain and then VMCA will replace SSL certificates of vCenter services.
26. Watch the certificate replacement message and make sure there are no errors.
Note, if Certificate manager failed to install new SSL certificates, it will rollback the changes and install old certs and will start services without any issues. Just wait for some time to start all services.
Get site nameCompleted [Replacing Machine SSL Cert...]
vlab-vc-site
Lookup all services
Get service vlab-vc-site:dc733106-31e4-4a48-b7ea-a0fdde9313bc
Update service vlab-vc-site:dc733106-31e4-4a48-b7ea-a0fdde9313bc; spec: /tmp/svcspec_UN174R
Get service vlab-vc-site:b91bc335-1d8d-46b8-8257-879474422483
Update service vlab-vc-site:b91bc335-1d8d-46b8-8257-879474422483; spec: /tmp/svcspec_dA3Ckh
Get service vlab-vc-site:7b9f83ed-c3da-4fd9-bed6-785fcf6a5019
Update service vlab-vc-site:7b9f83ed-c3da-4fd9-bed6-785fcf6a5019; spec: /tmp/svcspec_Wz_2kH
Get service 47c36d0a-bb88-486a-a0f5-eb7f32b8716b
Update service 47c36d0a-bb88-486a-a0f5-eb7f32b8716b; spec: /tmp/svcspec_jQc3Tm
Get service 1d1c2534-cb7e-42f9-99f2-5c08234179ee
Update service 1d1c2534-cb7e-42f9-99f2-5c08234179ee; spec: /tmp/svcspec_3CC3O_
Get service 5c7befd1-cd3b-40a1-b5da-e2ade5812fa8
Update service 5c7befd1-cd3b-40a1-b5da-e2ade5812fa8; spec: /tmp/svcspec_Gy2SCx
Get service b3c094a9-0e70-40fc-a213-b7c0f91208f4
Update service b3c094a9-0e70-40fc-a213-b7c0f91208f4; spec: /tmp/svcspec_tbdzvT
Get service aa81dd46-96f3-4d96-a055-cca9e2230e8e
Update service aa81dd46-96f3-4d96-a055-cca9e2230e8e; spec: /tmp/svcspec_IJPMbR
Get service 61bbcc34-9762-4517-8e57-f13ce25906b8
Update service 61bbcc34-9762-4517-8e57-f13ce25906b8; spec: /tmp/svcspec_uiMUqy
Get service 582aa620-b6d2-4e4f-8e3e-4d7dac838015
Update service 582aa620-b6d2-4e4f-8e3e-4d7dac838015; spec: /tmp/svcspec_mCTfhR
Get service a64b10d5-4a3f-4d5d-b370-a03e17887cc1
Update service a64b10d5-4a3f-4d5d-b370-a03e17887cc1; spec: /tmp/svcspec_bxOJ2K
Get service d3becf3f-c436-4f40-895e-8231fdbbeb38
Update service d3becf3f-c436-4f40-895e-8231fdbbeb38; spec: /tmp/svcspec_fS7RY1
Get service 61bbcc34-9762-4517-8e57-f13ce25906b8_authz
Update service 61bbcc34-9762-4517-8e57-f13ce25906b8_authz; spec: /tmp/svcspec_CbuXPJ
Get service a106c4af-1a97-41ad-9832-0ed06b31c32e
Update service a106c4af-1a97-41ad-9832-0ed06b31c32e; spec: /tmp/svcspec_YJvG5j
Get service ae8a88e1-1566-4fa7-972d-f892575dc108
Update service ae8a88e1-1566-4fa7-972d-f892575dc108; spec: /tmp/svcspec_6LAnr3
Get service 3010064d-717f-45e6-ac0d-4e2ab4063eb4
Update service 3010064d-717f-45e6-ac0d-4e2ab4063eb4; spec: /tmp/svcspec_qbll2S
Get service b3722397-a2d0-49dc-9106-2ddcc5db0e06
Update service b3722397-a2d0-49dc-9106-2ddcc5db0e06; spec: /tmp/svcspec_BgGjx1
Get service bfca6b85-0021-4ee5-84f7-275fcd4fac53
Update service bfca6b85-0021-4ee5-84f7-275fcd4fac53; spec: /tmp/svcspec_WGHmFK
Get service 3a74e01e-613c-4db8-a363-a2af7a63f073
Update service 3a74e01e-613c-4db8-a363-a2af7a63f073; spec: /tmp/svcspec_HxXApQ
Get service b5d47110-e534-46e3-915d-071bcbee5a80
Update service b5d47110-e534-46e3-915d-071bcbee5a80; spec: /tmp/svcspec_yGFJrp
Get service 8a94eb91-4096-48b9-b52d-20e030e9d063
Update service 8a94eb91-4096-48b9-b52d-20e030e9d063; spec: /tmp/svcspec_VlitkR
Get service 61bbcc34-9762-4517-8e57-f13ce25906b8_kv
Update service 61bbcc34-9762-4517-8e57-f13ce25906b8_kv; spec: /tmp/svcspec_Ym7LU3
Get service 72798453-18c0-4558-9bfe-bd2cd281621f
Update service 72798453-18c0-4558-9bfe-bd2cd281621f; spec: /tmp/svcspec_MEXsl8
Get service a64b10d5-4a3f-4d5d-b370-a03e17887cc1_com.vmware.vsan.health
Don't update service a64b10d5-4a3f-4d5d-b370-a03e17887cc1_com.vmware.vsan.health
Get service f32bcd6e-a903-4abe-b86d-09b37f1b6611
Update service f32bcd6e-a903-4abe-b86d-09b37f1b6611; spec: /tmp/svcspec_aT5C2O
Get service 209bfaf2-5e74-469d-bd14-f8bce3c67431
Update service 209bfaf2-5e74-469d-bd14-f8bce3c67431; spec: /tmp/svcspec_6O_TjH
Get service 8d954074-5555-4676-946c-add534bd22f1
Update service 8d954074-5555-4676-946c-add534bd22f1; spec: /tmp/svcspec_YGBFci
Updated 26 service(s)
Status : 100% Completed [All tasks completed successfully]
With this we have successfully configured VMCA as Subordinate CA of internal Microsoft CA and replaced SSL certificates of All vCenter services.
27. Now open the URL of vCenter server to see if it has valid certificate. You can notice the Lock icon of SSL certificate of URL, also see the issued By and Issued to details.
28. See the certificate Chain, you should see the Certificates of your Root CA in chain.
Now login to vCenter web client and make sure all Services are running fine.
Also you can login to vCenter web client with Administrator@vsphere.local account and go to Certificate Authority to view root Certificate, In Use certs, Issued or revoked certificates.
In my next post, I will share some common errors which we may get while replacing SSL certificates.
Thanks…!
Failed to start the virtual machine. The specified device is not a valid physical disk device
In ESXi 6, if you try to Power On Virtual machine you may get below Error.
The specified device is not a valid physical disk device.
An error was received from the ESX host while powering on VM VM-name.
Failed to start the virtual machine.
Module Disk power on failed.
Cannot open the disk '/vmfs/volumes/4f15231a-c162b6a6-0c01-5ef3fcc2c22b/vm-name/vm-name1.vmdk' or one of the snapshot disks it depends on.
The specified device is not a valid physical disk device
Also if you try to consolidate Virtual machine disk, you will receive below error.
The virtual disk is either corrupted or not a supported format.
Issue
You encounter this issue if you have configured ESXi scratch location at the root location of Local datastore or SAN datastore instead of folder on datastore.
e.g. /vmfs/volumes/datastore-name
Workaround
Take snapshot of Vm and delete it and immediately try to Power On. This will not fix the issue permanently.
Permanent fix
Reconfigure scratch location on ESXi host and point it to folder inside datastore.
e.g. /vmfs/volumes/datastore1-uuid/esxi1-scratch
1. Login to vCenter or ESXi Host.
2. Browse the datastore where you want to configure Scratch Location.
3. Create new folder for specific esxi Host e.g. esxi01-scratch
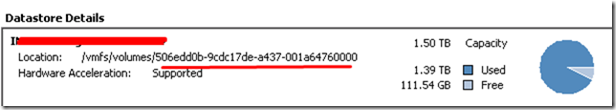
4. Get the datastore UUID
From ESXI configuration, select the datastore and from the datastore details note down the datastore UUID.
5. Select ESXi Host and go to Configuration –> Advance settings.
From Advance settings, select ScratchConfig
6. Enter the Folder path created on datastore to configure scratch location in tab of ScratchConfig.ConfiguredScatchLocation
e.g. /vmfs/volumes/506edd0b-9cdc17de-a437-001a64760000/esxi-scratch
7. Click on OK.
8. Put ESXi Host in Maintenance mode.
9. Restart ESXi host.
Thanks…!
Thursday, 26 May 2016
vCenter SQL Agent Jobs on SQL Always ON or Mirrored SQL
If you are using Microsoft SQL Always ON or Mirrored SQL then you need to create vCenter SQL Agent jobs on both primary and secondary SQL servers. During installation of vCenter server it only create Agent jobs on the primary SQL Instance.
You need to manually create vCenter SQL Agent Jobs on secondary SQL instance. Refer below KB for manually creating vCenter SQL Agent Jobs.
Once you have Jobs created on both the SQL servers, we need to make sure SQL jobs run only on primary SQL server. Because the database will keep running on primary sql server and if Jobs run secondary instance, they are going to fail.
To avoid failure of vCenter SQL agent Jobs, put the condition in Job scripts to Run a SQL Job only when that SQL server is primary SQL instance.
You need to put this condition in all vCenter SQL agent Jobs and on both the primary and secondary SQL servers.
Thanks…!
Cannot mount vmfs volume
If ESXi detect the LUN incorrectly then it do not allow to mount the VMFS volume without deleting exiting VMFS volume and formatting LUN.
In below Image we can see, Keep the existing signature and Assign a new signature Options are grayed out and only Format the disk option is available.
If we select Format the disk option, all the VMs will get deleted from VMFS volume.

Solution
We need to mount such VMFS volumes forcefully.
1. Login to ESXi host using local shell or using SSH with root username and password.
2. Find VMFS volume ID of affected LUN.
#esxcfg-volume –l
3. Then Mount VMFS volume with UUID.
#esxcfg-volume -M UUID
e.g. #esxcfg-volume –M 5135cc26-5a43cc6d-34c7-0025b5990306
This will forcefully mount existing VMFS volume on ESXi Host and then you can use this volume to run VMs.
See this KB for more information -
Thanks….!
Wednesday, 25 May 2016
vRealize Automation - Migrate vCenter to vCSA
In this post we will see how to migrate Windows based vCenter to vCSA ( vCenter Server Appliance) which is used as backend for vRealize Automation ( formally known as vCAC).
Currently most of the organization are using Windows based vCenter (vCS) as a backend for vRealize Automation. We will use VMware’s vCS to vCSA convertor to migrate Windows vCenter 5.5 to vCSA 5.5 and then will upgrade vCSA 5.5 to vCSA 6.0 update 2.
Test setup -
- vCenter Server 5.5 – all vCenter components running on same Windows system
- vRealize automation 6.2.2.0 – distributed installation of vRA components like app server, iaas, proxy, manager servers….etc. vRealize has its own SSO server.
- vRealize Orchestrator 6.0.3
- Make sure your test setup is similar to your production setup and works fine– off course with couple of ESXi Host and VMs. Nested ESXi will also work.
So Before we make any changes in Production, we need to test everything in Test Environment.
As per VMware documents during vCS to vCSA migration it will preserve vCenter's UUID, MoRef and all ESXi Host, Clusters, VM, datastore, Network should be same for vRA to work post migration.
Migration Task –
Before making changes in production setup, take backup of all required servers, DB so that we can revert back to old working state if we run in to any issues.
- Backup vRA DB
- Shutdown all servers of vRealize Automation and vRO.
- Take snapshot of all vRA servers.
- Backup vCenter SQL DB
- Take snapshot of vCenter VM.
Migrate Windows based vCenter to vCenter Appliance ( vCS to vCSA Migration )
- Download vCenter to vCenter Application migration (vCS to vCSA ) Fling from VMware site.
https://labs.vmware.com/flings/vcs-to-vcva-converter
VCS Migration Appliance Document v0.9.1
- Deploy vCS to vCSA migration fling on vCenter or ESXi Host.
- Deploy vCenter 5.5 Appliance.
- Using Fling appliance do the migration from vCS to vCSA.
- Upgrade vCSA 5.5 to vCenter 6.x
Step by Step Process to Upgrade VCSA 5.5 to VCSA 6
- Make sure vCenter and all vCenter Components are running fine after upgrade.
Start vRealize automation -
- Start vRealize automation servers and vRO.
- Test vRealize functionality by deploying VMs, creating blueprint…..etc
- Test vRO.
if you face issue with vRO then remove vRO from vRA and add again or re-register vRO with vCenter.
Thanks…!
Tuesday, 24 May 2016
Unable to get signed certificate for host
While trying to add ESXi host in vCenter 6, you may get below error.
Error -
A general system error occurred: Unable to get signed certificate for host: <HOSTNAME>. Error: Failed to connect to the remote host, reason = rpc _s_too_many_rem_connects (0x16c9a046).
Reason -
This error occurs if you have replaced SSL certificates of VMware vCenter Server using VMCA and made VMCA as an Intermediate Certificate Authority.
Solution -
Once you make VMCA as an intermediate Certificate authority, you need to wait for 24 hours to add new ESXi Host in vCenter.
This behavior is changed in VMware vCenter 6.0 Update 2 and later with the advanced setting vpxd.certmgmt.certs.minutesBefore
Login to vCenter server using Administrator credentials, Go to vCenter server settings and update key vpxd.certmgmt.certs.minutesBefore value to 10.
Workaround -
You can wait for 24 hours to add new Host in vCenter server or Add ESXi Hosts in vCenter before making VMCA as an Intermediate CA
Thanks…!
Provide vCenter permissions to Domain Users
This Post is part of VMware vSphere Install, Configure, Manage Training.
Make sure you have added vCenter server in Domain and Added Active Directory as identity source in SSO to proceed with providing permissions. If not Please complete previous task first.
1. Login to vCenter using web client and with Administrator@vsphere.local username/password.
2. Go to Home of web client –> select vCenter Instance –> then Click on Manage Tab.
3. Click on Permission Tab –> Click on + Green icon to provide permission to users.
4. Select the Role which you want to provide to new Users. In this case I have provided Administrator role. You can also create custom roles and permissions for users.
5. Click on Add Button in Add Permission pop up window
Select domain from which you want to add users.
You can search user or group name from search Box.
Select users/group and click on Add
6. Click OK to close Select Users/Groups Window.
As per your requirements you check or uncheck Propagate to Children Check box.
In this case I want to propagate permission to all child objects.
7. Click ok to close Add permission process.
8. Now with this, we have provided permission to Windows Users,
Open new browser and open web client to login vCenter server.
Enter your domain Username as domain-name\user-name and enter password to login to web client.
Thanks…!
What’s Next - Add ESXi Host in vCenter